In maternal health, gestational diabetes is a term with relative frequency. At May-Grant OB-GYN, serving the areas of Lancaster, PA, we believe in empowering women with knowledge. Let’s explore understanding gestational diabetes’s causes, implications, management, and beyond.
Gestational Diabetes Demystified
Gestational diabetes is a form of high blood sugar affecting pregnant women. This condition, generally emerging in the later stages of pregnancy, may pose certain risks if not managed correctly. However, with proper care and guidance, most mothers successfully navigate their pregnancy journey.
Understanding the Cause
During pregnancy, hormonal shifts are par for the course. Some of these hormones impede the action of insulin, a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels. This insulin resistance phenomenon can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, culminating in gestational diabetes.
The Potential Implications
While gestational diabetes might seem daunting, it’s essential to understand its implications to manage it effectively. Knowledge is, after all, the first step toward a solution.
- Risks to the Mother: The most direct impact of gestational diabetes falls on the mother. This condition may lead to a higher likelihood of high blood pressure during pregnancy and an increased chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life.
- Risks to the Baby: Elevated blood sugar levels in the mother can also influence the baby’s health. These implications could range from the baby growing larger than usual, leading to potential difficulties during delivery, to the risk of the baby developing low blood sugar immediately after birth.
Screening and Diagnosis
Recognizing the importance of early detection, we at May-Grant OB-GYN endorse regular screenings for gestational diabetes.
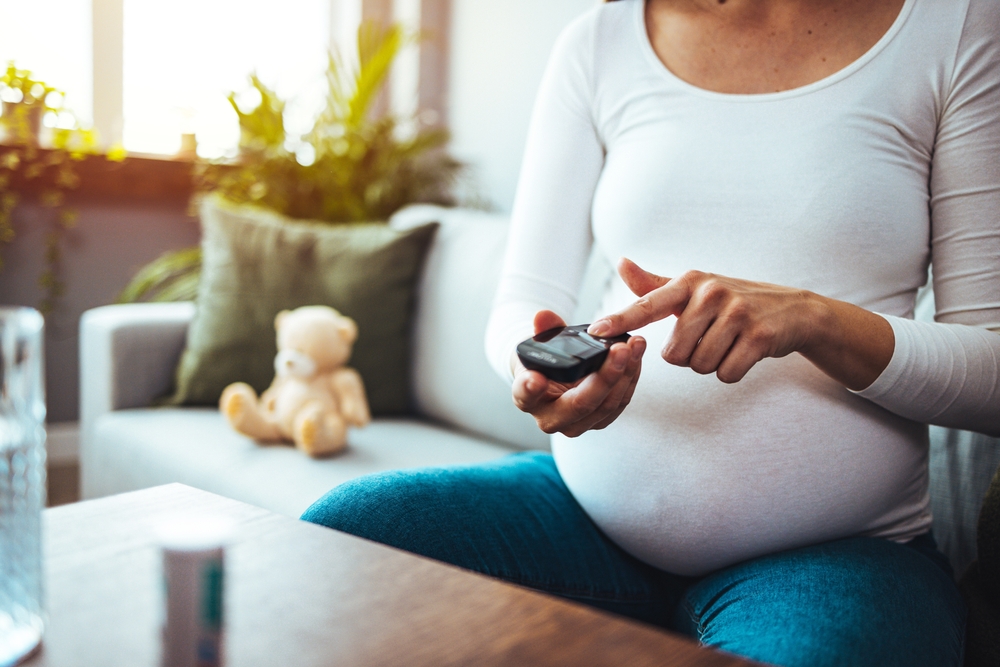
- The Glucose Challenge: Typically performed between the 24th and 28th weeks of pregnancy, the glucose challenge involves consuming a sugary drink followed by a blood test an hour later. This test measures how efficiently your body processes sugar.
- The Glucose Tolerance Test: If the glucose challenge test shows high blood sugar levels, the next step is the glucose tolerance test. This more detailed test involves overnight fasting, followed by blood sugar measurements at various intervals after consuming a sugary drink.
Managing Gestational Diabetes
Having gestational diabetes doesn’t mean you cannot have a healthy pregnancy. With proper care and attention, you can keep your blood sugar levels in check and ensure your and your baby’s well-being.
- Tailored Nutrition Plans: One of the primary steps toward managing gestational diabetes is adopting a balanced and nutritious diet. It’s all about smart food choices – opting for complex carbohydrates over simple sugars, prioritizing fiber-rich foods, and evenly spreading carbohydrates throughout the day.
- Regular Physical Activity: Exercise can significantly help maintain optimum blood sugar levels. Regular physical activity encourages your body to use glucose, even in the face of insulin resistance. However, always consult with your healthcare provider to design an exercise routine that is safe for both you and your baby.
- Monitoring Blood Sugar Levels: Frequent monitoring of your blood sugar levels helps track your condition’s progress. Your healthcare provider will guide you on how often to check your blood sugar and the ideal targets you should aim for.
- Medication If Necessary: In some cases, diet and exercise might not be enough to keep blood sugar levels in check. In such instances, your healthcare provider might prescribe insulin therapy or other medications to manage your gestational diabetes.
Life Post Gestational Diabetes
While gestational diabetes resolves after childbirth, it does signal a heightened risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future. However, healthy lifestyle choices can significantly reduce this risk and set the stage for long-term well-being. Some examples include:
- Healthy Lifestyle Habits: Embracing a balanced diet and regular exercise routine is not just about managing gestational diabetes—it is a commitment to your health. Maintaining these habits, post-pregnancy can significantly reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Post gestational diabetes, routine health check-ups become more crucial than ever. These allow for early detection and management if your blood sugar levels begin to rise again.
- Breastfeeding, A Protective Measure: Breastfeeding offers numerous benefits for both mother and baby. For mothers with a history of gestational diabetes, breastfeeding can help regulate blood sugar levels post-childbirth and contribute to weight loss.
The Takeaway
Gestational diabetes, while seemingly intimidating, is a condition that many women successfully manage, resulting in healthy pregnancies and deliveries. Being informed is the cornerstone of this success. Understanding your body, recognizing the implications of gestational diabetes, knowing the steps for its management, and taking strides for long-term health are all part of the journey.
Remember, you are not alone in this journey. At May-Grant OB-GYN, we stand as your steadfast companions, guiding you through each phase, empowering you with knowledge, and providing expert care tailored to your needs. Gestational diabetes is but a part of your pregnancy journey, and with the right care, it can be navigated successfully, leading to the joy of welcoming your new baby into the world.
Sources:
- American Diabetes Association. (2020). Gestational Diabetes.
- Mayo Clinic. (2020). Gestational Diabetes.
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2020). Gestational Diabetes and Pregnancy.